Chemistry 9 Solved Paper 2018 Overseas Federal Board
Federal Board, Class 9 Chemistry Solved Past Paper 2018 Overseas is given below. The paper is solved according to the reduced syllabus for the annual examination 2021. Chemistry 9 Solved Paper 2018 Overseas is solved using the recommended textbook.
Chemistry 9 Solved Paper 2018 Overseas
Section A
Q1. MCQs
Chemistry 9 Solved Paper 2018 Overseas
Section B
Q2. Attempt any ELEVEN parts. The answer of each part should not exceed 3 to 4 lines.
(i) Calculate the number of molecules present in 3.4 moles of Ammonia (NH3).
Sol. Number of moles of Ammonia (NH3) = 3.4 moles
Avogadro’s Number = NA = 6.022 x 1023
Number of molecules =?
Formula: Number of molecules = Number of moles x NA
Number of molecules = 3.4 x 6.022 x 1023
Number of molecules = 20.47 x 1023
Number of molecules = 2.047 x 1024 molecules
(ii) The atomic number of an element is 26 and its mass number is 56.
a. How many protons and electrons do an atom of this element has?
b. How many neutrons does this atom has? Draw Bohr’s model of this element.
Ans. Atomic number = 26
Atomic mass = 56
a) Number of protons =?
Number of electrons =?
b) Number of neurons =?
Bohr model =?
Number of protons = Number of electrons = Atomic number
Number of protons = 26
Number of electrons = 26
Number of neutrons = Atomic mass – Atomic number
Number of neutrons = 56 – 26
Number of neutrons = 30
Bohr Model

(iii) Electronic configuration of atoms of some elements are given below. Classify them into groups and period.
a. 1s2 2s2
b. 1s2 2s2 2p3
c. 1s2 2s2 2p5
Ans. (a) The electronic configuration = 1s2, 2s2
Valence shell has configuration = 2s2
Period number = 2
Group number = 2
Thus, given electronic configuration belongs to an element present in the 2nd Period of Group IIA.
(b) The electronic configuration = 1s2, 2s2, 2p3
Valence shell has configuration = 2s2, 2p3
Period number = 2
Group number = 2 + 3 = 5
Thus, given electronic configuration belongs to an element present in the 2nd Period of Group VA.
(c) The electronic configuration = 1s2, 2s2, 2p5
Valence shell has configuration = 2s2, 2p5
Period number = 2
Group number = 2 + 5 = 7
Thus, given electronic configuration belongs to an element present in the 2nd Period of Group VIIA.
(iv) Which element has higher shielding effect, Ca or Sr and why?
Ans. Sr has a higher shielding effect.
Since the shielding effect increases down the group, therefore, Sr will have a higher shielding effect as compared to Ca because Sr is just below the Ca in the 2nd group of the Period table.
(v) How do epoxy adhesives stick to other substance? Give the reason.
Excluded from Syllabus
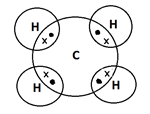
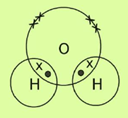
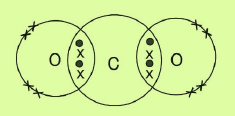
(vi) Make Lewis dot structure of the following compounds:
a. CH4
b. H2O
c. CO2
Ans. a. CH4
b. H2O
c. CO2
(vii) Water boils at 120°C in a pressure cooker. Why?
Ans. A pressure cooker is equipped with a valve that controls the pressure inside the pot. This valve generally exerts a pressure of 2 atm. Therefore, the valve does not allow water vapours to escape until the pressure inside the pot reaches 2 atm. Because vapour pressure of water becomes 2 atm when the temperature reaches 120°C. So, water boils at 120°C in a pressure cooker.
(viii) Why is methanol soluble in water but benzene is not?
Excluded from Syllabus
(ix) Differentiate between spontaneous and non-spontaneous process with the help of examples.
Excluded from Syllabus
(x) List three uses of electrolytic cell.
Ans. 1. It is used for the purification of copper.
2. It is used to electroplate metals such as tin, silver, nickel, etc on steel.
3. It is used to prepare anodized aluminum which can absorb dyes.
(xi) Identify more metallic element in each pair of elements. Give the reason.
a. K; Na
b. Be; Na
c. Be; B
Ans. (a) Potassium (K) is more metallic than sodium (Na) because Potassium is placed lower than Na in the group so electro-positivity increases in the group.
(b) Na is more metallic than Be because electro-positivity increases from top to bottom in group.
(c) Electro-positivity decreases in period so Be is more metallic than B as we move from left to right.
(xii) Find the oxidation state of Sulphur ‘S’ in the following compounds:
a. H2S
b. H2SO4
c. Na2S2O3
Sol. a. H2S
2 (+1) + x = 0
+2 + x = 0
x = – 2
b. H2SO4
2 (+1) + x + 4 (–2) = 0
+2 + x – 8 = 0
x – 6 = 0
x = +6
c. Na2S2O3
2 (+1) + 2x + 3(–2) = 0
+2 + 2x – 6 = 0
2x – 4 = 0
2x = +4
x = +4 / 2
x = +2
(xiii) How is ozone important for us? Give reason.
Excluded from Syllabus
(xiv) How does evaporation lower the temperature of a liquid?
Ans. Evaporation is a process in which a liquid changes into vapours. During the process of evaporation, the high-energy molecules start to escape from the liquid surface. As a result, the average kinetic energy of the remaining molecules decreases. Due to this decrease in kinetic energy the temperature of the liquid also decreases. Hence evaporation lowers the temperature of liquids.
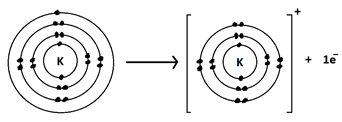
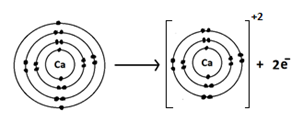
(xv) Represent the formation of cations for the following metal atoms by electron dot structures:
a. Na
b. K
c. Ca
Ans.
a. Na
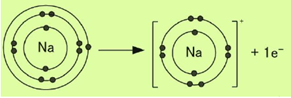
b. K
c. Ca
Chemistry 9 Solved Paper 2018 Overseas
Section C
Attempt any TWO questions. All questions carry equal marks.
Q3. a. Define covalent bond and illustrate the formation of covalent bond with the help of suitable examples. (6)
Ans. Covalent Bond
The chemical bond formed by the mutual sharing of electrons between two atoms is called a covalent bond.
Consider the formation of a covalent bond in the hydrogen molecule. A hydrogen atom has a single valence electron. Two hydrogen atoms share their valence electrons to form a diatomic molecule.
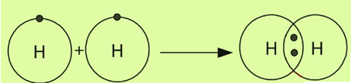
Consider the formation of a covalent bond in a nitrogen molecule. A nitrogen atom has five valence electrons. Two nitrogen atoms share their three valence electrons to form a diatomic molecule.
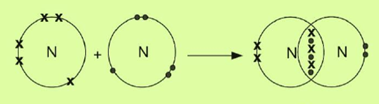
Consider the formation of covalent bonds in a methane molecule. A carbon atom has four valence electrons. Four hydrogen atoms share their single electron with four electrons of the carbon atom to form four single bonds.
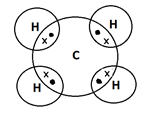
Q3. b. Why iron metal is hard and sodium is soft? Interpret with the help of electronic configuration of both metals. (4)
Ans. The reason is that in iron, metal atoms are tightly packed due to their small size. They are held through strong metallic bonds due to many electrons in the valence shell. Whereas sodium consists of bigger atoms. Because of their large size and only one electron, sodium atoms have weak metallic bonds. Thus, sodium is a soft metal.
Q4. a. Define solubility. Elaborate the factors that affect solubility with the help of suitable examples. (6)
Ans. Solubility
The amount of solute that dissolves in 100 g of a solvent at a particular temperature is called its solubility.
Effect of temperature on solubility:
Change of temperature can change the solubility of a solute in a solvent. It may increase or decrease.
Effect on solubility of Ionic Compounds:
1. Solubility of an ionic compound generally increases with rise in temperature.
Example: Solubility of ionic compounds such as KNO3, KCI, AgNO3, and KI increases with rise in temperature.
2. Solubility of some solids decreases with rise in temperature.
Example: The solubility of Na2SO4 decreases with rise in temperature.
3. Solubility of some solids is little affected with rise in temperature.
Example: Solubility of NaCI in water is least affected by rise in temperature.
Effect on solubility of Gases: Solubility of gases decreases with rise in temperature.
Example: Solubility of oxygen and air decreases with rise in temperature.
Q4. b. Calculate the number of molecules in 0.50 moles of methane (CH4). (4)
Sol. Number of moles of methane (CH4) = 0.50 moles
Avogadro’s Number = NA = 6.022 x 1023
Number of molecules =?
Formula: Number of molecules = Number of moles x NA
Number of molecules = 0.50 x 6.022 x 1023
Number of molecules = 3.011 x 1023 molecules
Q5. a. Explain electrolytic refining of copper with the help of diagram and chemical reactions that take place during the process. (6)
Excluded from Syllabus
Q5. b. Alkali metals belong to S-block of the periodic table. Why? Give suitable examples in support of your answer. (4)
Ans: The group-IA elements except hydrogen are known as alkali metals. They belong to S-block because these elements have a general electronic configuration of ns1 in their valence shell. For example, lithium, sodium, and potassium have 1 electron in their s sub-shells.


